Colloidal Tunable Metasurfaces via Depletion-Induced Self-Assembly of Plasmonic Nanorods
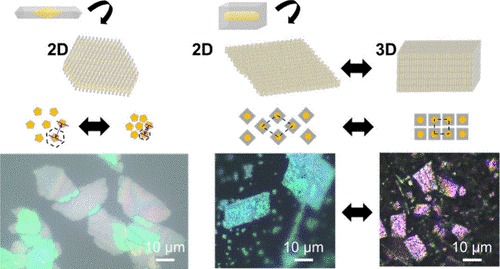 |
03/11/2025 Self-assembly offers a scalable approach to creating nanostructures with tunable properties, particularly for plasmonic materials. Conventional self-assembly often produces dense 3D supercrystals, which restrict light and analyte accessibility. By contrast, directing assembly into 2D metasurfaces increases active surface area and promotes collective optical responses, making them highly promising for sensing and photocatalysis. While metasurfaces are typically immobilized on interfaces, here we introduce the concept of “colloidal metasurfaces”, which are liquid-dispersed and reconfigurable assemblies. Specifically, we exploit depletion-induced self-assembly (DISA) to reversibly organize anisotropic plasmonic nanorods (Au@Ag) into colloidal metasurfaces. By tuning the depletion strength, we achieve dimensional control between 2D and 3D arrangements and modulate the compacity of the colloidal assemblies from 21% to 80%. Assemblies of nanorods with different cross sections reveal shape-dependent reconfigurability: pentagonal rods maintain hexagonal lattice symmetry, whereas square rods undergo symmetry shifts from rhombic to square. These colloidal metasurfaces support multiple assembly–disassembly cycles without loss of optical function and enable modulation of Raman scattering through lattice parameter tuning. Together, this work establishes a functional, reconfigurable colloidal platform for plasmonic metasurfaces using shape-directed DISA. |